생성자 함수(constructor)
new 연산자와 함꼐 호출하여 객체(인스턴스)를 생성하는 함수
여러가지 빌트인 생성자 함수
// String 생성자 함수에 의한 String 객체 생성
const strObj = new String('Lee');
console.log(typeof strObj); // object
console.log(strObj); // String {"Lee"}
// Number 생성자 함수에 의한 Number 객체 생성
const numObj = new Number(123);
console.log(typeof numObj); // object
console.log(numObj); // Number {123}
// Boolean 생성자 함수에 의한 Boolean 객체 생성
const boolObj= new Boolean(true);
console.log(typeof boolObj); // object
console.log(boolObj); // Boolean {true}
// Function 생성자 함수에 의한 Function 객체(함수) 생성
const func = new Function('x', 'return x * x');
console.log(typeof func); // function
console.dir(func); // ƒ anonymous(x)
// Array 생성자 함수에 의한 Array 객체(배열) 생성
const arr = new Array(1, 2, 3);
console.log(typeof arr); // object
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3]
// RegExp 생성자 함수에 의한 RegExp 객체(정규 표현식) 생성
const regExp = new RegExp(/ab+c/i);
console.log(typeof regExp); // object
console.log(regExp); // /ab+c/i
// Date 생성자 함수에 의한 Date 객체 생성
const date = new Date();
console.log(typeof date); // object
console.log(date); // Mon May 04 2020 08:36:33 GMT+0900 (대한민국 표준시)
객체 리터럴에 의한 객체 생성 방식의 문제점
한번에 하나의 객체만 생성. 객체를 여러 개 생성해야 하는 경우 매번 같은 프로퍼티를 기술해야해서 비효율적.
객체는 프로퍼티를 통해 객체 고유의 상태(state)를 표현
메서드를 통해 상태 데이터인 프로퍼티를 참조하고 조작하는 동작(behavior)을 표현.
생성자 함수(객체(인스턴스)를 생성하는 함수)에 의한 객체 생성 방식
// 생성자 함수
function Circle(radius) {
// 생성자 함수 내부의 this는 생성자 함수가 생성할 인스턴스를 가리킨다.
this.radius = radius;
this.getDiameter = function () {
return 2 * this.radius;
};
}
// 인스턴스의 생성
const circle1 = new Circle(5); // 반지름이 5인 Circle 객체를 생성
const circle2 = new Circle(10); // 반지름이 10인 Circle 객체를 생성
console.log(circle1.getDiameter()); // 10
console.log(circle2.getDiameter()); // 20
this 바인딩?
인스턴스 반환
function Circle(radius) {
// 1. 암묵적으로 인스턴스가 생성되고 this에 바인딩된다.
// 2. this에 바인딩되어 있는 인스턴스를 초기화한다.
this.radius = radius;
this.getDiameter = function () {
return 2 * this.radius;
};
// 3. 완성된 인스턴스가 바인딩된 this가 암묵적으로 반환된다
}
// 인스턴스 생성. Circle 생성자 함수는 암묵적으로 this를 반환한다.
const circle = new Circle(1);
console.log(circle); // Circle {radius: 1, getDiameter: ƒ}
암묵적으로 this를 반환하는데
명시적으로 객체를 반환하면 암묵적인 this 반환이 무시됨.
하지만 원시 값을 반환하면 무시되고 암묵적으로 this가 반환됨.
return문은 반드시 생략
내부 메서드 [[Call]]과 [[Construct]]
함수 객체는 일반 객체가 가지고 있는 내부 슬롯과 내부 메서드를 모두 가지고 있다
// 함수는 객체다.
function foo() {}
// 함수는 객체이므로 프로퍼티를 소유할 수 있다.
foo.prop = 10;
// 함수는 객체이므로 메서드를 소유할 수 있다.
foo.method = function () {
console.log(this.prop);
};
foo.method(); // 10
일반 객체는 호출할 수 없지만 함수는 호출할 수 있다.
함수 객체만을 위한 [[Environment]], [[FormalParameters]] 등의 내부 슬롯과
[[Call]], [[Constrcut]] 같은 내부 메서드를 추가로 가지고 있다.
함수가 일반 함수로서 호출되면 함수 객체의 내부 메서드 [[Call]]이 호출되고 new 연산자와 함께 생성자 함수로서 호출되면 내부 메서드 [[Construct]]가 호출된다.
function foo() {}
// 일반적인 함수로서 호출: [[Call]]이 호출된다.
foo();
// 생성자 함수로서 호출: [[Construct]]가 호출된다.
new foo();
함수 객체는 [[call]]이 있지만 [[Construct]]는 있을수고 없을수도 있음
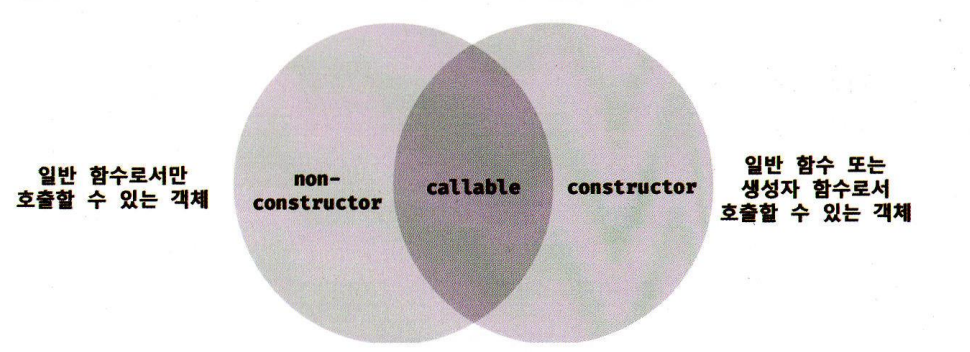
constructor와 non-constructor 구분
함수가 어디에 할당되어 있는지가 아니라 함수 정의 방식에 따라 구분한다.
constuctor : 함수 선언문, 함수 표현식, 클래스
non-constructor : 메서드(ES6 메서드 축약 표현), 화살표 함수
// 일반 함수 정의: 함수 선언문, 함수 표현식
function foo() {}
const bar = function () {};
// 프로퍼티 x의 값으로 할당된 것은 일반 함수로 정의된 함수다. 이는 메서드로 인정하지 않는다.
const baz = {
x: function () {}
};
// 일반 함수로 정의된 함수만이 constructor이다.
new foo(); // -> foo {}
new bar(); // -> bar {}
new baz.x(); // -> x {}
// 화살표 함수 정의
const arrow = () => {};
new arrow(); // TypeError: arrow is not a constructor
// 메서드 정의: ES6의 메서드 축약 표현만을 메서드로 인정한다.
const obj = {
x() {}
};
new obj.x(); // TypeError: obj.x is not a constructor
일반 함수와 생성자 함수로 호출 했을 때의 차이와 굳이 나누는 이유??
// 생성자 함수
function Circle(radius) {
this.radius = radius;
this.getDiameter = function () {
return 2 * this.radius;
};
}
// new 연산자 없이 생성자 함수 호출하면 일반 함수로서 호출된다.
const circle = Circle(5);
console.log(circle); // undefined
// 일반 함수 내부의 this는 전역 객체 window를 가리킨다.
console.log(radius); // 5
console.log(getDiameter()); // 10
circle.getDiameter();
// TypeError: Cannot read property 'getDiameter' of undefined일반 함수와 생성자 함수에 특별한 형식적 차이는 없다.
따라서 생성자 함수의 첫 문자를 대문자로 기술하는 파스칼 케이스로 구분.
new.target
생성자 함수가 new 연산자 없이 호출되는 것을 방지해더라도 언제나 실수는 발생 할 수 있다.
new.target은 this와 유사하게 constructor인 모든 함수 내부에서 암묵적인 지역 변수와 같이 사용 되며
메타 프로퍼티라고 부름.
new 연산자와 함께 호출되면 함수 내부의 new.target은 함수 자신을 가리킨다.
new 연산자 없이 일반 함수로서 호출된 함수 내부의 new.target은 undefined다.
new로 호출 안했으면 재귀로 생성자 함수로서 호출 가능
// 생성자 함수
function Circle(radius) {
// 이 함수가 new 연산자와 함께 호출되지 않았다면 new.target은 undefined다.
if (!new.target) {
// new 연산자와 함께 생성자 함수를 재귀 호출하여 생성된 인스턴스를 반환한다.
return new Circle(radius);
}
this.radius = radius;
this.getDiameter = function () {
return 2 * this.radius;
};
}
// new 연산자 없이 생성자 함수를 호출하여도 new.target을 통해 생성자 함수로서 호출된다.
const circle = Circle(5);
console.log(circle.getDiameter()); // 10
대부분의 빌트인 생성자 함수 (Object, String, Number, Boolean, Function, Array, Date, RegExp, Promise 등)
는 new 연산자와 함께 호출되었는지를 확인한 후 적절한 값을 반환한다.
Object와 Function 생성자 함수는
new 연산자 없이 호출해도 new 연산자와 함께 호출했을 때와 동일하게 동작.
let obj = new Object();
console.log(obj); // {}
obj = Object();
console.log(obj); // {}
let f = new Function('x', 'return x ** x');
console.log(f); // ƒ anonymous(x) { return x ** x }
f = Function('x', 'return x ** x');
console.log(f); // ƒ anonymous(x) { return x ** x }
String, Number, Boolean 생성자 함수는
new 연산자 없이 호출하면 문자열, 숫자, 불리언 값을 반환.
이를 통해 데이터 타입을 반환하기도 한다.
const str = String(123);
console.log(str, typeof str); // 123 string
const num = Number('123');
console.log(num, typeof num); // 123 number
const bool = Boolean('true');
console.log(bool, typeof bool); // true boolean'JavaScript > Deep Dive' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 19 프로토타입 (1) (1) | 2024.09.26 |
|---|---|
| 18 함수와 일급 객체 (0) | 2024.09.26 |
| 16 프로퍼티 어트리뷰트 (0) | 2024.09.23 |
| 15 let, const 키워드와 블록 레벨 스코프 (0) | 2024.09.23 |
| 14 전역 변수의 문제점 (0) | 2024.09.20 |


